Azimuthal Inversion Applied to Fracture Characterization Study:A Presalt Case Study, Brazil
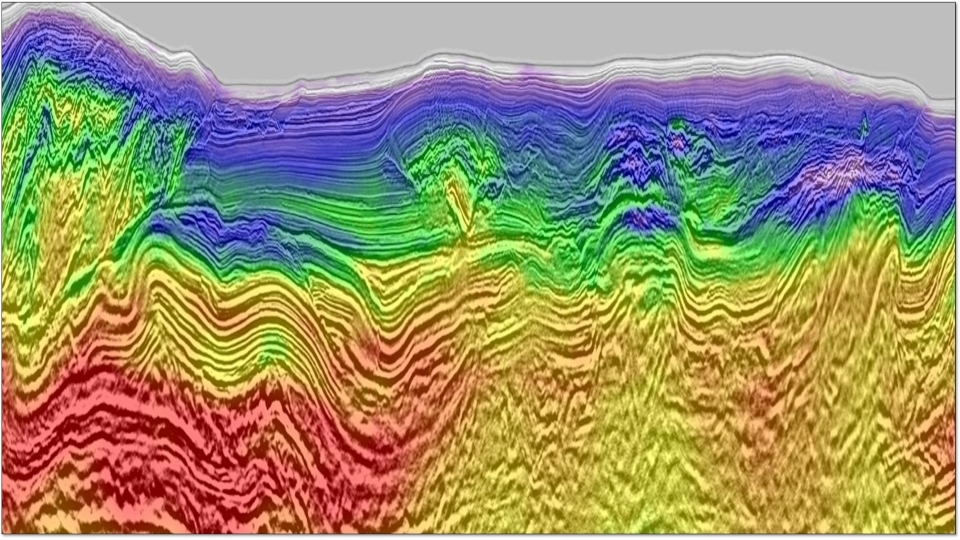
In recent years, the Brazilian presalt characterization has been a challenging task, either because of the imaging problems associated with complex salt layer geometry (Penna et al., 2019) or due to large heterogeneity in the presalt carbonates reservoir (Oliveira et al., 2018). Some efforts to address these challenges include full-azimuthal acquisitions technologies (nodes acquisition) and new processing techniques and studies to better understanding the geological model. Recent multi-azimuthal seismic data acquisition provides not only better seismic imaging, but also fractures properties through velocity and amplitude changes with azimuth variation, providing a better spatial characterization of the fracture system. We present an azimuthal elastic seismic inversion (Roure et al., 2012) in a Nodes presalt reservoir data, addressing the local fracture system characterization. Fracture parameters are described in terms of the normal and tangential weakness plus fracture strike. Prior to the inversion, an azimuthal seismic preconditioning has also performed on the seismic dataset to attenuate the imaging problems in the reservoir interval and consequently improving the signal-to-noise ratio providing better estimates of the properties of interest. Fracture characterization studies commonly integrates borehole image logs, core data and well test, usually restrict to specific areas around drilled wells. In some cases, tridimensional fracture models are created through geostatistical modelling constrained by seismic attributes. However, those are indirect measures of fractures, with high associated uncertainties. Recent multi-azimuthal seismic data acquisition provides not only better seismic imaging, but also fractures properties through velocity and amplitude changes with azimuth variation, providing a better spatial characterization of the fracture system. We present an azimuthal elastic seismic inversion (Roure et al., 2012) in a Nodes presalt reservoir data, addressing the local fracture system characterization. Fracture parameters are described in terms of the normal and tangential weakness plus fracture strike. Prior to the inversion, an azimuthal seismic preconditioning has also performed on the seismic dataset to attenuate the imaging problems in the reservoir interval and consequently improving the signal-to-noise ratio providing better estimates of the properties of interest.