Angle-dependent Water Column Statics Correction through Sparse TauP Inversion
Angle-dependent Water Column Statics Correction through Sparse TauP Inversion
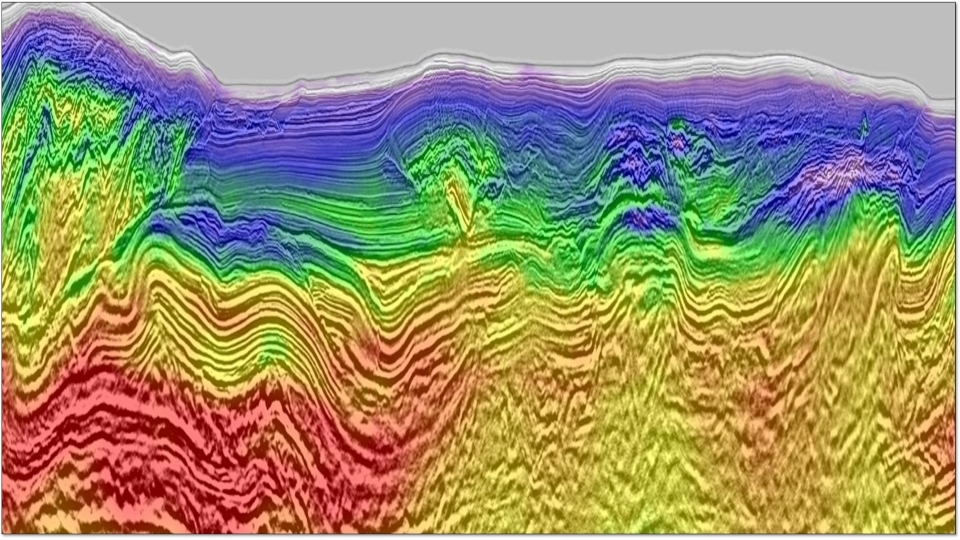
Water column statics caused by tidal variation and water velocity change during seismic surveys is one major source of noise in marine 4D projects. Correction of this statics effect is a key step in any marine 4D processing. Applying water column statics correction requires ...