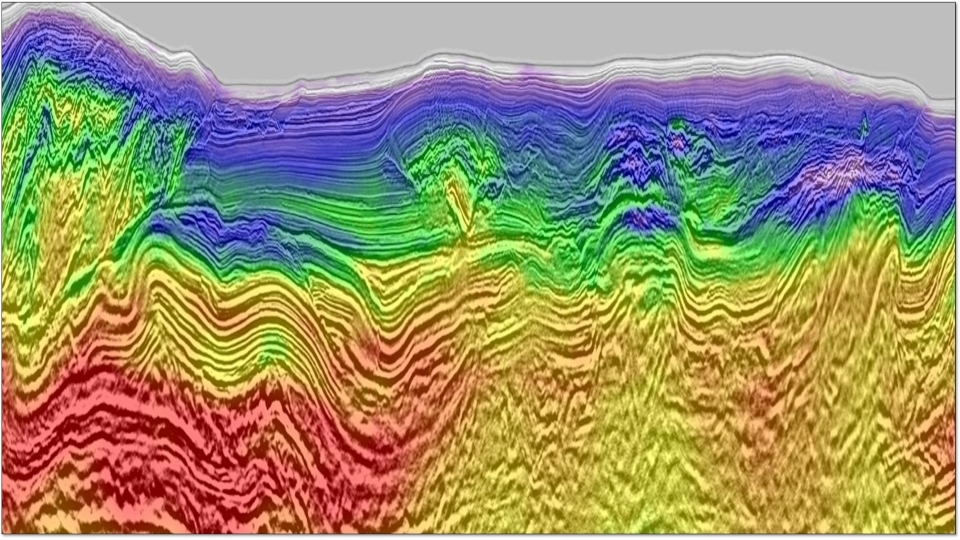
In shallow water environments, water-layer related multiples (WLRMs) typically dominate other classes of multiple, and achieving effective attenuation of WLRMs is of significant interest. When combined with an appropriate adaptive subtraction, Model-based Water-layer Demultiple (MWD) has been found to be highly effective in attenuating ...
Technical Content
Joint Low-rank and Sparse Inversion for Multidimensional Simultaneous Random/Erratic Noise Attenuation and Interpolation
Joint Low-rank and Sparse Inversion for Multidimensional Simultaneous Random/Erratic Noise Attenuation and Interpolation
Several methods have been proposed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio by attenuating incoherent noise, including prediction error filtering (Canales 1984), projection filtering (Soubaras 1995), and more recently rank reduction filtering. In this last category, we can differentiate eigenimage filtering (Trickett 2003), Cadzow / Singular ...
Improved subsalt images with shot patch-based angle gather illumination weighting
Improved subsalt images with shot patch-based angle gather illumination weighting
One way to address the problem of weak subsalt illumination is through angle gather illumination weighting (AGILW). In this technique, synthetic data mimicking the field data are generated and migrated the same way as the field data. Illumination weighting scalars are obtained by measuring ...
Ray-tracing-based Input Data Selection RTM - A Target Oriented Approach for Clearer Subsalt Image
Ray-tracing-based Input Data Selection RTM - A Target Oriented Approach for Clearer Subsalt Image
We present an input data selection workflow based on 3D ray-tracing to improve the RTM image in areas of poor illumination and low signal-to-noise ratio. It is effective for imaging subsalt three-way closure with weak subsalt primaries and strong noise levels. The workflow can ...
Simultaneous Shooting for Sparse OBN 4D Surveys and Deblending Using Modified Radon Operators
Simultaneous Shooting for Sparse OBN 4D Surveys and Deblending Using Modified Radon Operators
Discusses use of simultaneous-source acquisition for sparse (ROV-deployed) OBN surveys, using time and motion studies to quantify impact on acquisition time. Also describes new technique for sim-src crosstalk noise attenuation using modified Radon operators. Finally, application to Gorgon OBN data for baseline and monitor ...
Multiple timelapse realisations produced using wavefield separation, data selection, or diverging processing flows are combined using powerful noise-reducing data weights formulated using the 3D images as well as the 4D differences. The result separates 4D signal from incoherent 4D noise and also 4D noise ...
Non-linear Slope Tomography for Orthorhombic Pre-stack Time Imaging
Non-linear Slope Tomography for Orthorhombic Pre-stack Time Imaging
In the context of WAZ data the VTI hypothesis is not always sufficient for insuring focusing of time migration. We propose an extension of non-linear slope tomography for time imaging to the orthorhombic case. We use a model of orthorhombic anisotropy parameterized by five ...
The seismic image represents the spatially variable reflectivity of the medium where migration effectively rotates the wavelet to be normal to the imaged reflectors. While this is the general case, it is often disregarded, and one-dimensional spectral analysis of the vertical coordinate is commonly ...
Estimation of primaries by sparse inversion in shallow water: Practical challenges and strategies
Estimation of primaries by sparse inversion in shallow water: Practical challenges and strategies
Estimation of primaries by sparse inversion (EPSI) is an iterative method that effectively separates primaries and surface-related multiples, especially in shallow water. Multiple attenuation in shallow water is challenging, mainly because of acquisition limitations. We propose a strategy for EPSI with the following objectives ...